Inconel 625 vs Inconel 825: Key Differences, Properties & Industrial Uses
When a subsea pipeline in an offshore installation began showing early signs of corrosion fatigue, the materials team revisited a decision made years earlier. The alloy had passed initial corrosion tests, but under cyclic stress, elevated temperatures, and chloride exposure, it was slowly losing integrity.
The lesson was not about poor material quality—it was about material suitability. For industries like oil & gas, chemical processing, marine, and power generation, choosing between Inconel 625 and Inconel 825 can determine whether a system lasts decades or fails prematurely.
This guide explains the real differences, properties, and industrial uses of these two nickel alloys—so decisions are based on data, not assumptions.
Overview of Inconel Alloys
Inconel alloys are nickel-based superalloys designed for extreme environments involving high temperatures, mechanical stress, and corrosion. While both Inconel 625 and Inconel 825 offer excellent corrosion resistance, they are engineered for different performance priorities.
Understanding these distinctions is critical for engineers and procurement teams operating in high-risk conditions.
Chemical Composition & Strengthening Mechanisms
Inconel 625 (UNS N06625)
- Nickel (Ni): ~58%
- Chromium (Cr): 20–23%
- Molybdenum (Mo): 8–10%
- Niobium (Nb): 3.15–4.15%
Strength Mechanism: Solid-solution strengthening from molybdenum and niobium
Result: Very high mechanical strength without heat treatment
Inconel 825 (UNS N08825)
- Nickel (Ni): 38–46%
- Chromium (Cr): 19.5–23.5%
- Molybdenum (Mo): 2.5–3.5%
- Copper (Cu): 1.5–3%
Strength Mechanism: Corrosion resistance through balanced alloying
Result: Moderate strength with superior resistance to acidic environments
Key Insight: Inconel 625 has nearly twice the yield strength of Inconel 825 at room temperature.
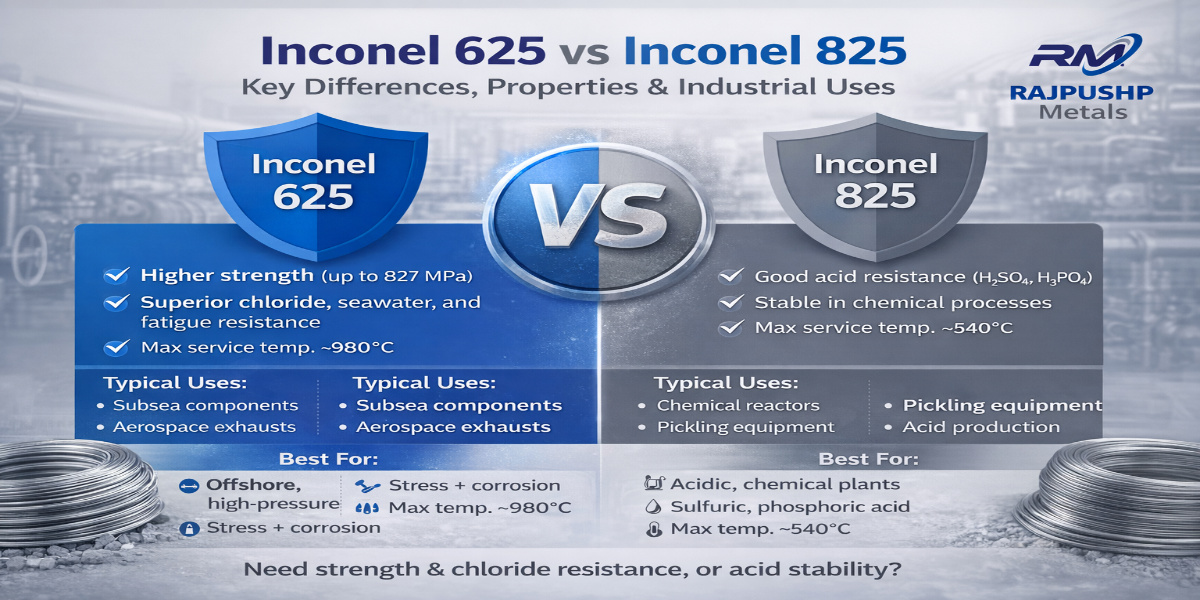
Mechanical Properties Comparison
| Property | Inconel 625 | Inconel 825 |
|---|---|---|
| Yield Strength | ~414 MPa | ~220 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | ~827 MPa | ~586 MPa |
| Maximum Service Temperature | ~980°C | ~540°C |
| Fatigue Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
According to ASM International, Inconel 625 maintains mechanical integrity well beyond 800°C, while Inconel 825 is better suited for lower-temperature corrosive services.
Corrosion Resistance: Where Each Alloy Excels
Inconel 625
- Chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking resistance
- Excellent performance in seawater and subsea environments
- Ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature systems
- Handles combined fatigue and corrosion effectively
Inconel 825
- Outstanding resistance to sulfuric and phosphoric acids
- Excellent in nitric acid environments
- Ideal for chemical reactors and pickling plants
- Best for moderate temperature acidic services
Studies indicate that alloys with higher molybdenum content—such as Inconel 625—offer up to 40% better resistance to localized corrosion in chloride-rich environments.
Industrial Applications
Typical Uses of Inconel 625
- Offshore risers and subsea components
- Aerospace exhaust systems
- Heat exchangers under cyclic loading
- Nuclear and high-pressure piping
Typical Uses of Inconel 825
- Chemical processing vessels
- Acid production and handling units
- Pollution control equipment
- Pickling tanks and heat exchangers
In most projects, the decision comes down to whether mechanical stress or chemical exposure is the dominant risk factor.
Key Buyer Considerations
- Will mechanical loads fluctuate over time?
- Is chloride exposure combined with pressure or vibration?
- Is corrosion uniform or localized?
- What is the expected lifecycle—5 years or 25 years?
Rajpushp Metal helps customers choose the right Inconel grade with full material traceability, certifications, and application-based guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is Inconel 625 stronger than Inconel 825?
Yes. Inconel 625 has significantly higher yield and tensile strength.
2. Which alloy is better for acidic environments?
Inconel 825 performs better in sulfuric, phosphoric, and nitric acids.
3. Can Inconel 825 be used in marine environments?
It can be used, but Inconel 625 offers superior seawater and fatigue resistance.
4. Is Inconel 625 more expensive?
Yes, but its longer service life often results in lower lifecycle costs.
5. Which alloy has better weldability?
Both weld well, but Inconel 625 is often preferred for complex fabrications.
Conclusion
Choosing between Inconel 625 and Inconel 825 is not about which alloy is “better,” but which one best matches your operating conditions. Mechanical stress, temperature, and corrosion type should guide the decision. Selecting the correct alloy at the design stage ensures long-term reliability, safety, and cost efficiency.
